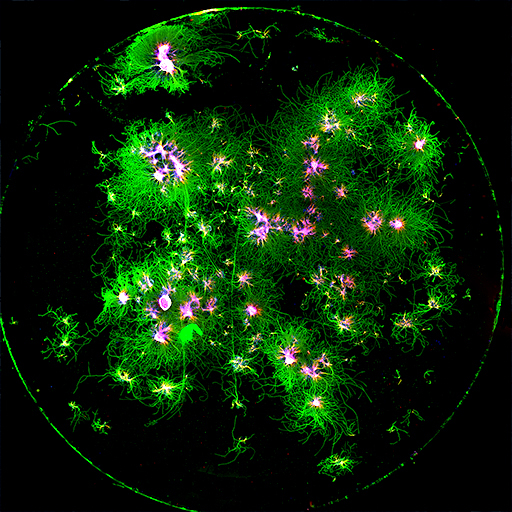
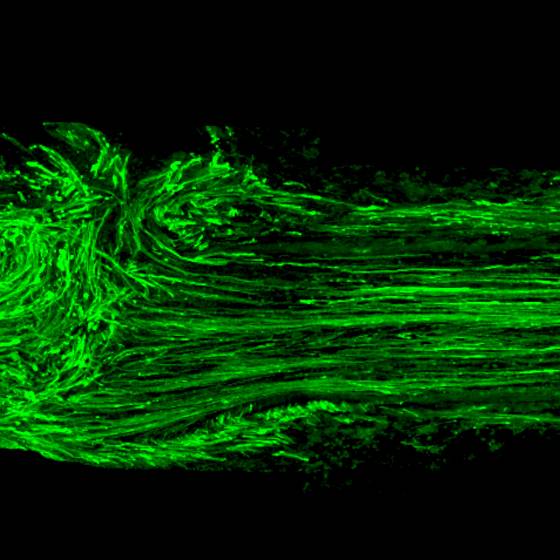
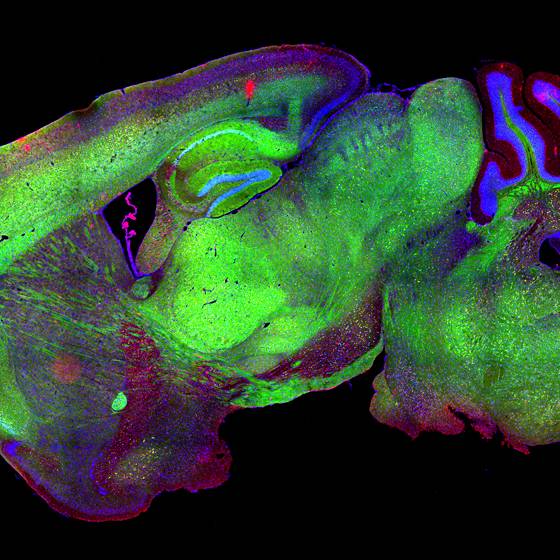
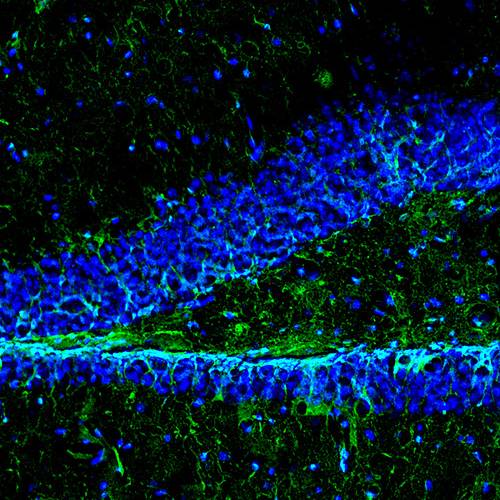
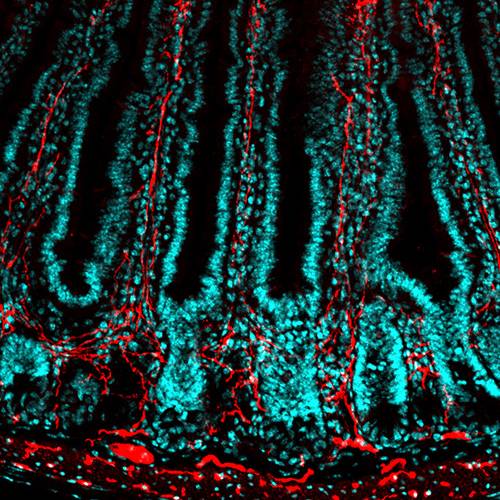
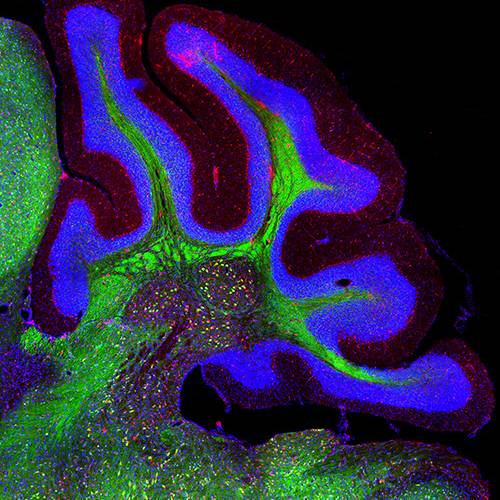
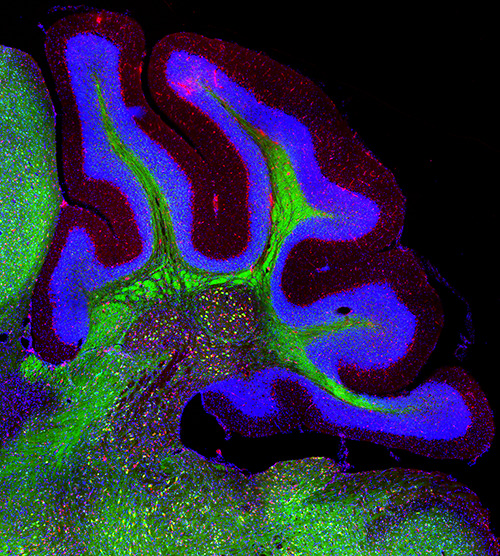
The gut-brain axis along aging
The gut microbiota plays an important role in the physiology of the central nervous system and inflammation. Brain-gut communication enables bidirectional modulatory effects between the microbiota and the central nervous system, which might be involved in physiological and pathological events. Changes in the intestinal microbiota during aging show a decrease in the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, presenting a higher proportion of Bacteroides, Clostridium, and Proteobacteria, and a decrease in Actinobacteria compared to young adults.
We are cultivating and analyzing thousands of bacterias from the Chilean population, in order to find new strains with positive effect over inflammation and aging.
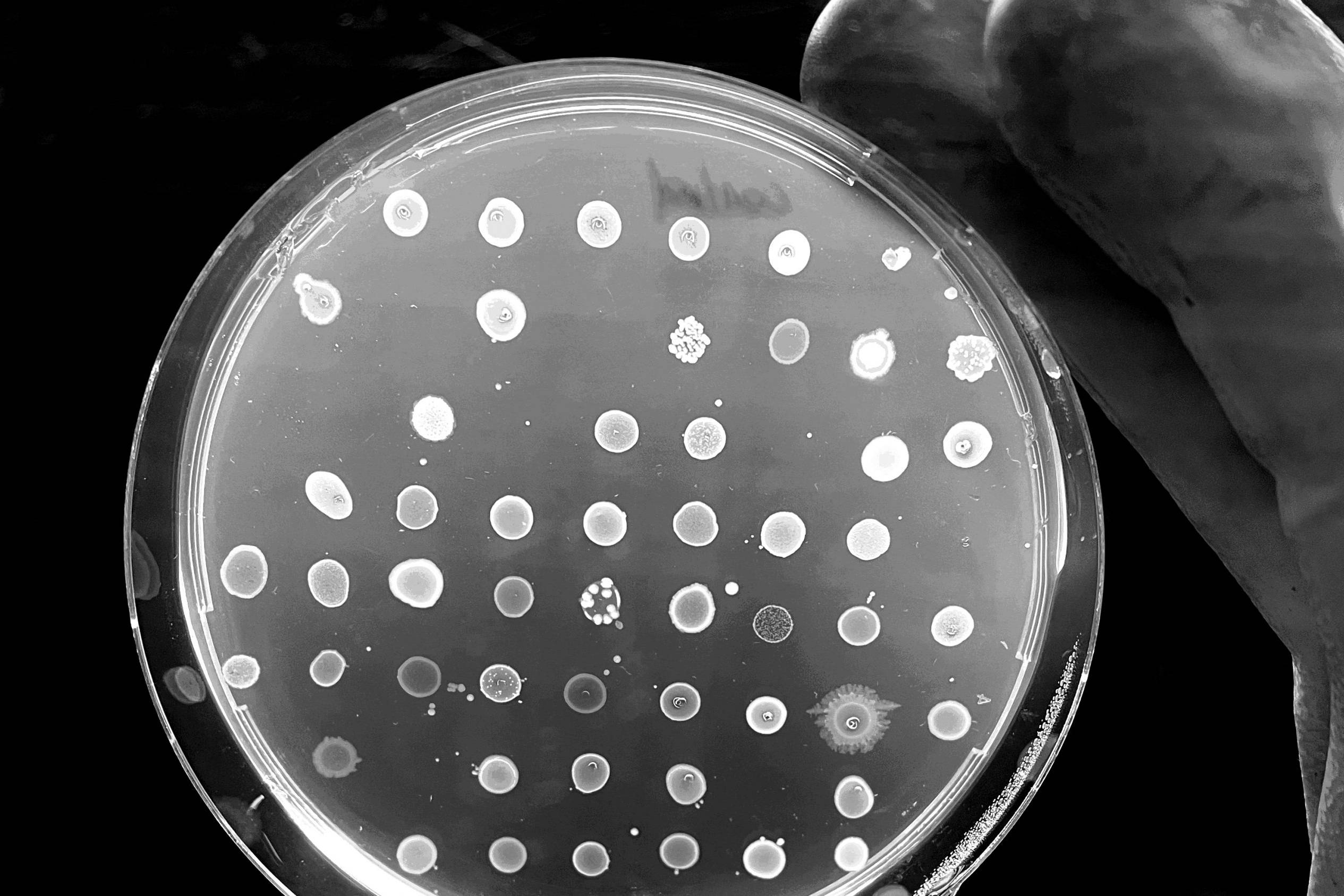
Restoring the gut microbiome for healthy aging
Our research focuses on the search for bacterial consortia with effect over the aging process. Our aim is to restore the intestinal microbiota during aging, converting it into a healthier and more beneficial intestinal microbiota. For the generation of bacterial consortia, we have generated a bank of bacteria isolated from the intestinal microbiota of healthy Chileans with a wide diversity of bacteria strains. Hundreds of these isolated and taxonomically classified bacteria has been evaluated for their probiotic properties and we are currently generating consortia for in vitro and in vivo studies. In addition, we are studying the gut microbiota in aged people, trying to correlate changes in their composition associated to the risk to develop brain conditions.
People involved
Related Publications
PUBLICATIONSDataNervous System FxPNSNeuroDegeneration
septiembre 30, 2021
Schwann cell to axon transfer of ribosomes: toward a novel understanding of the role of glia in the nervous system.
Court FA, Hendriks WT, MacGillavry HD, Alvarez J, van Minnen J.
J Neurosci. 2008 Oct 22;28(43):11024-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2429-08.2008.
PMID: 18945910
PUBLICATIONSDataNervous System FxPNS
septiembre 30, 2021
Alpha6beta4 integrin and dystroglycan cooperate to stabilize the myelin sheath.
Nodari A, Previtali SC, Dati G, Occhi S, Court FA, Colombelli C, Zambroni D, Dina G, Del Carro U, Campbell KP, Quattrini A, Wrabetz L, Feltri ML.
J Neurosci. 2008 Jun 25;28(26):6714-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0326-08.2008.
PMID: 18579745
PUBLICATIONSDataPNSNeuroDegeneration
septiembre 30, 2021
Remodeling of motor nerve terminals in demyelinating axons of periaxin-null mice.
Court FA, Brophy PJ, Ribchester RR.
Glia. 2008 Mar;56(4):471-9. doi: 10.1002/glia.20620.
PMID: 18205176
PUBLICATIONSDataNervous System FxPNS
septiembre 30, 2021
Beta1 integrin activates Rac1 in Schwann cells to generate radial lamellae during axonal sorting and myelination.
Nodari A, Zambroni D, Quattrini A, Court FA, D'Urso A, Recchia A, Tybulewicz VL, Wrabetz L, Feltri ML.
J Cell Biol. 2007 Jun 18;177(6):1063-75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200610014.
PMID: 17576799
Related News
Doctorado en Neurobiología dio inicio a su versión 2019 con charlas de destacados científicos
octubre 14, 2021
La cita contó con la exposición de la Premio Nacional de Ciencias 2006, Dra. Cecilia Hidalgo, quien reflexionó sobre la incorporación de la mujer al mundo de la ciencia. La bienvenida a la jornada la…
Curso internacional y Mini-simposio “Neuroinflammation in Health and Disease”
octubre 14, 2021
El Curso internacional y Mini-simposio “Neuroinflammation in Health and Disease”, va realizarse del 3 al 9 de abril en el Institut Pasteur de Montevideo, la Facultad de Medicina (Udelar) y el…