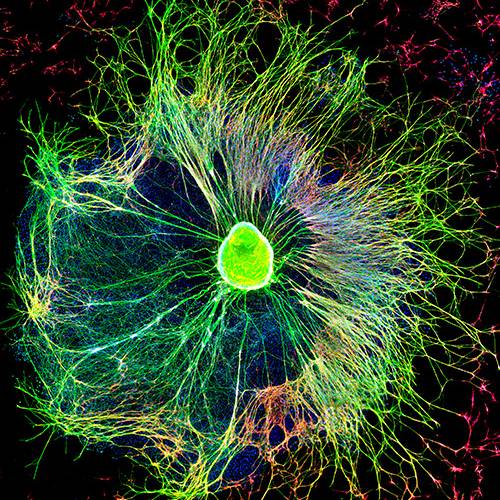
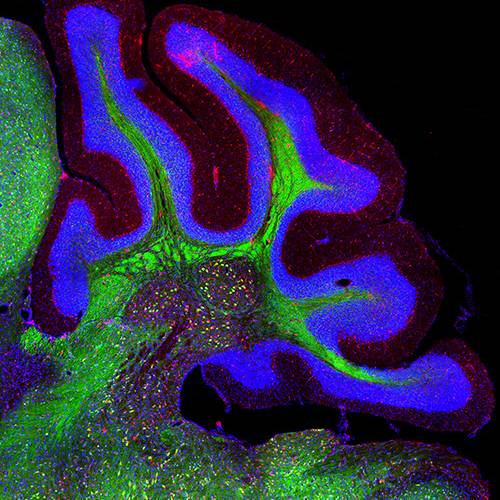
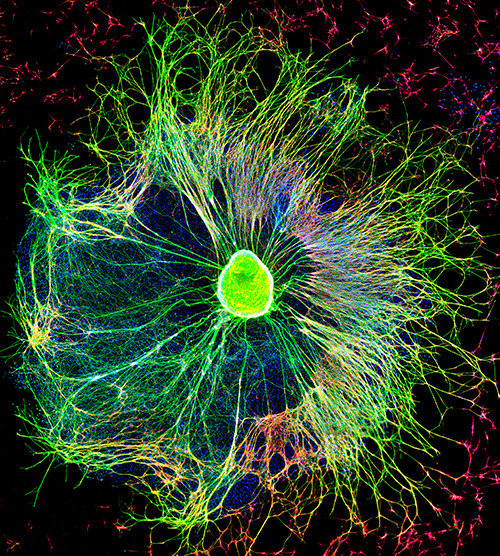
Axonal Degeneration as a target for neuroprotection
Destruction programs are cellular mechanisms that have survival value when they operate under physiological control, but their malfunction could be deleterious for the organism. Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a well-known physiological destruction mechanism most apparent during development but persisting throughout the organism’s life. Other destruction programs are emerging as physiological processes that may not terminate in the destruction of the whole cell but only of restricted cellular domains. In the case of neurons, pruning of exuberant branches of terminal arborizations and degeneration of axons severed from their cell bodies are outstanding examples. Importantly, axonal degeneration is an early event in neurodegenerative condition including Alzheimer´s and Parkinson disease, as well as peripheral neuropathies. We are interested to define molecular players in the process of axonal degeneration to find therapeutic targets for neuroprotection.
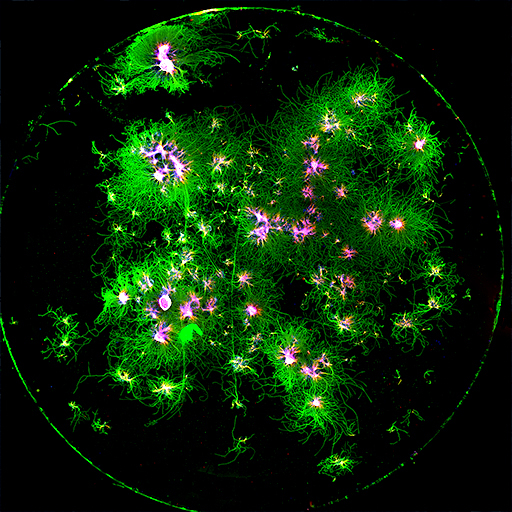
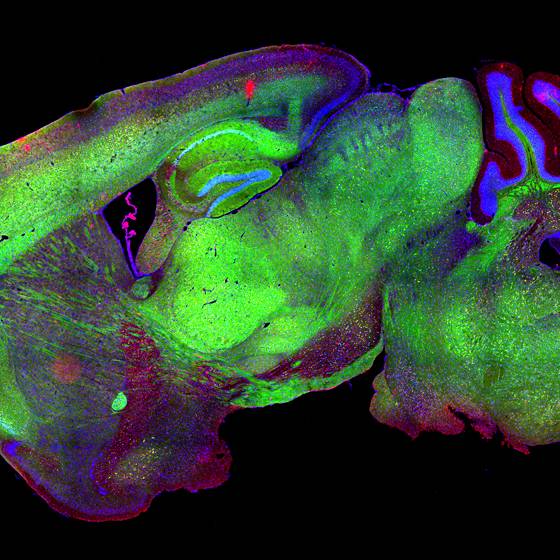
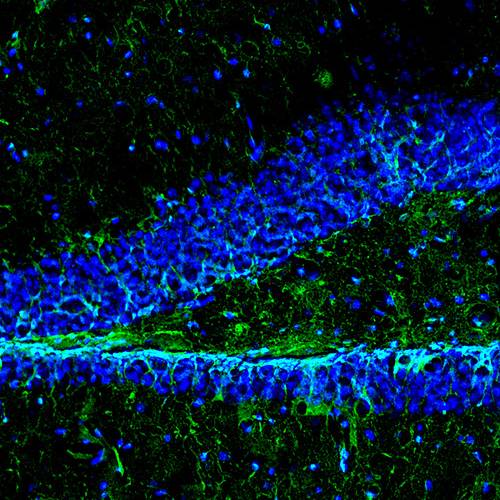
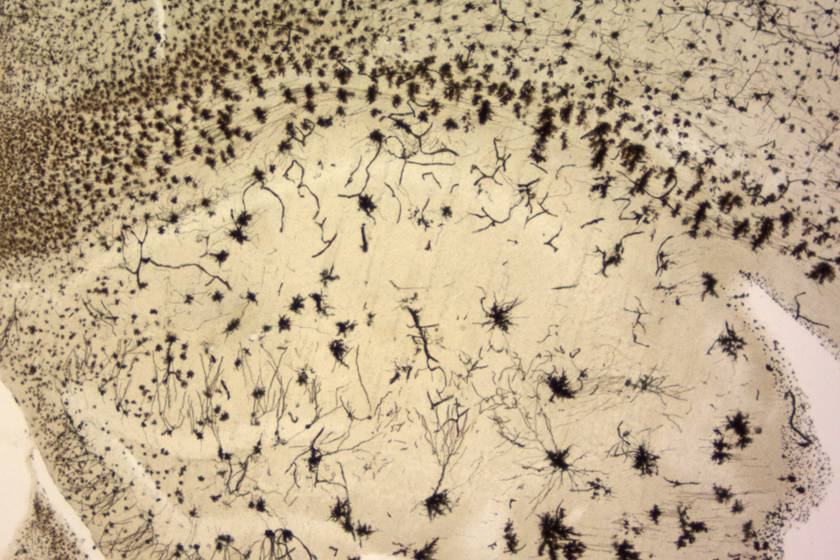
Golgi staining of a mouse hippocampal section, with this technique, sparse neuronal labelling is obtained, which allows detailed analysis of individual neurons.
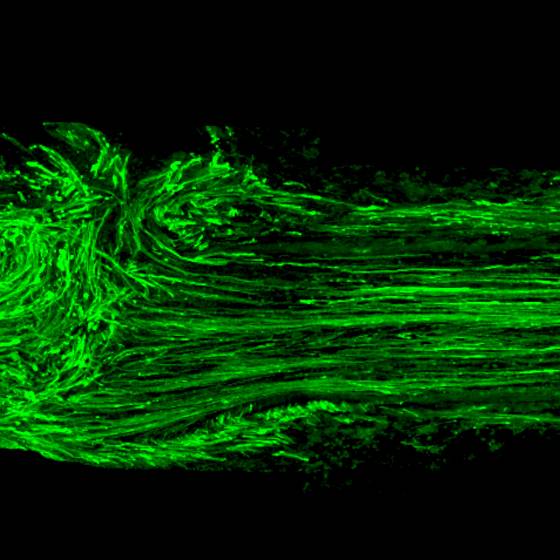
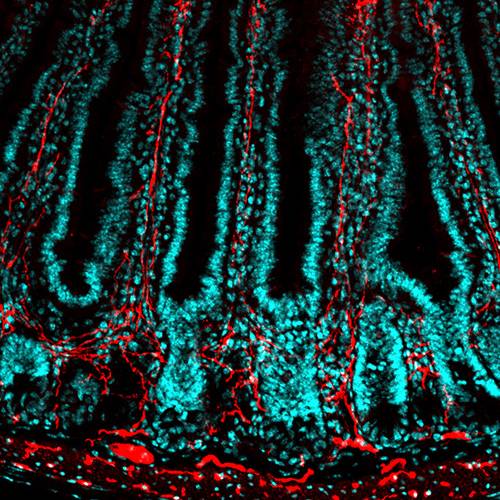
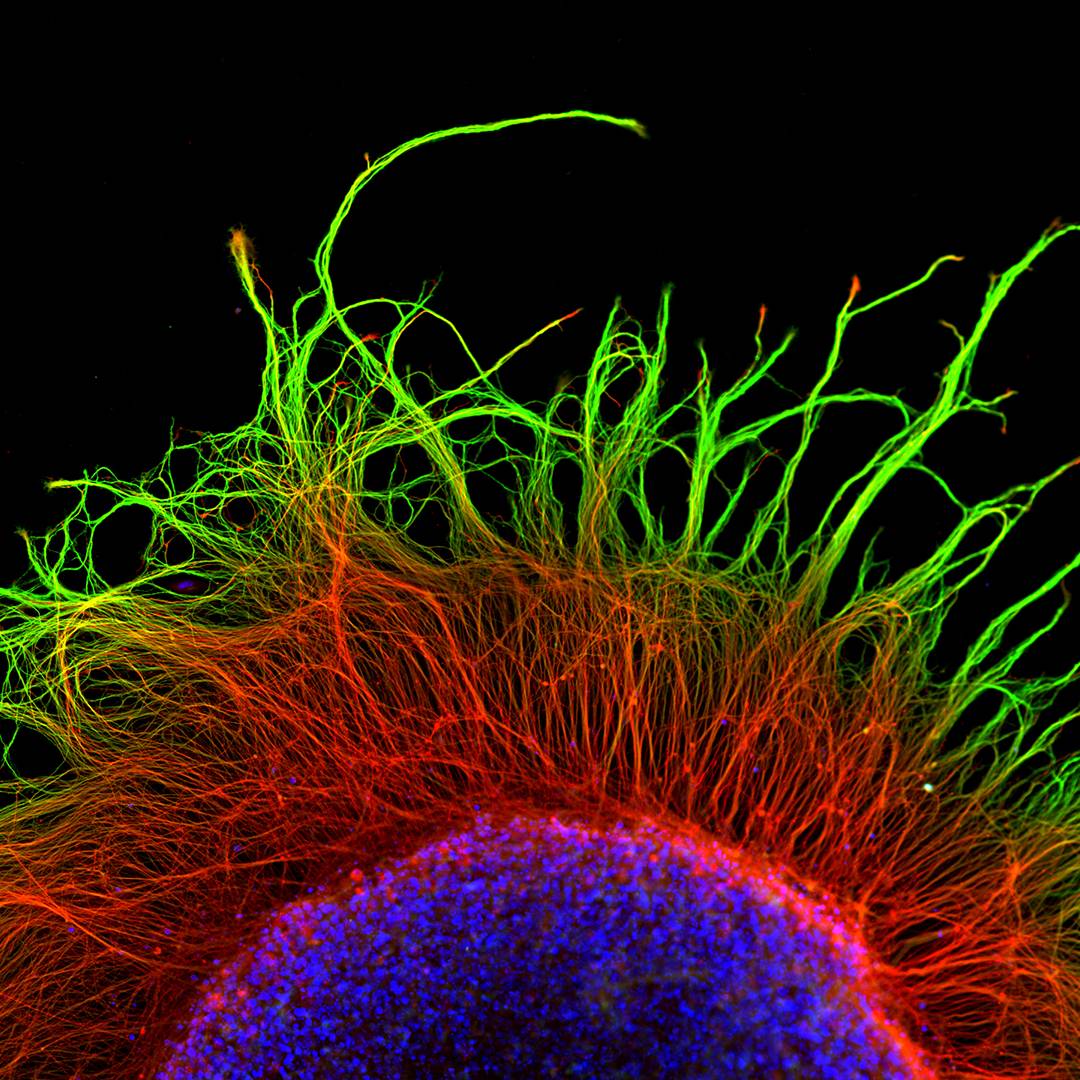
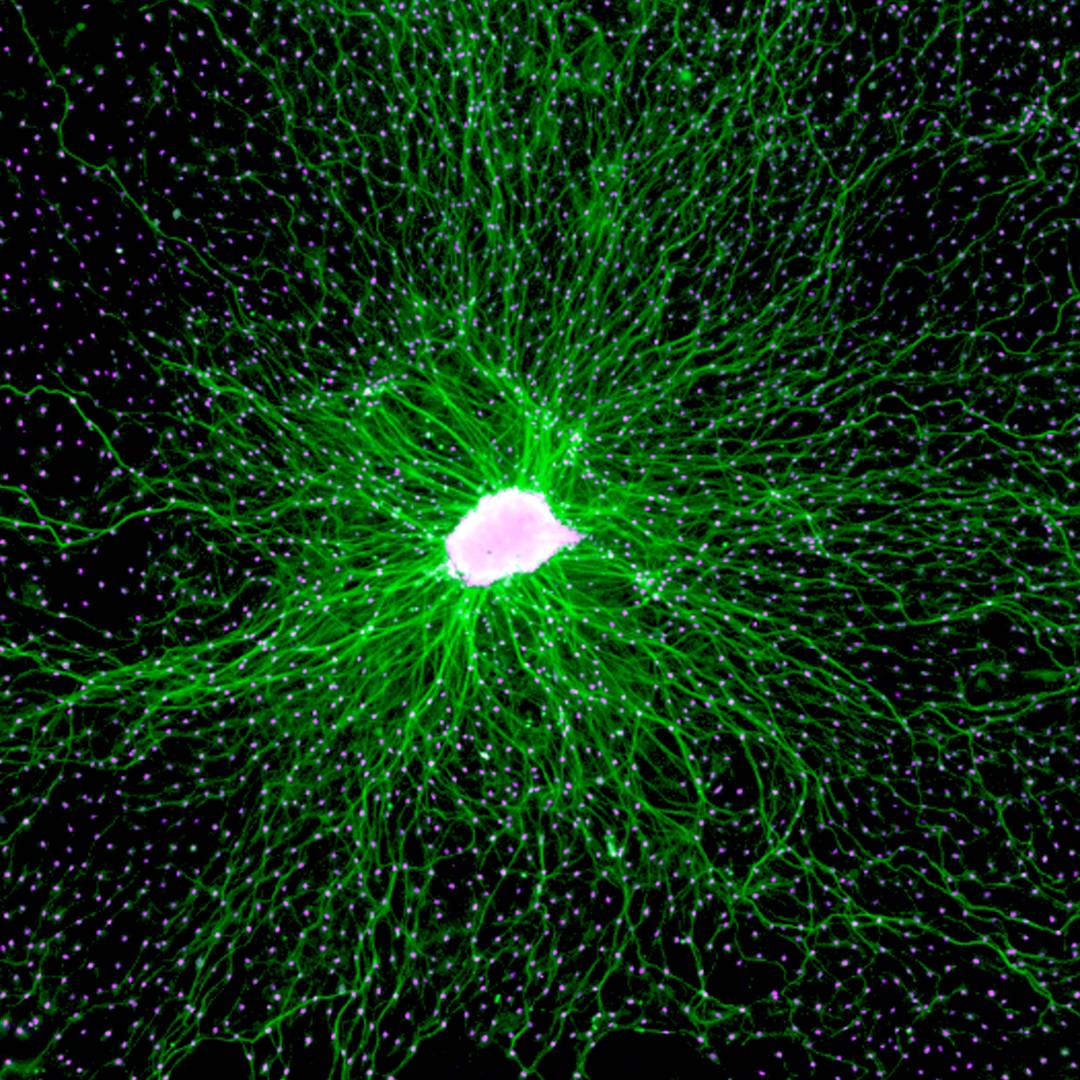
The degeneration of axons constitutes a salient feature shared by several neurodegenerative diseases that contributes to neuronal dysfunction and cell death. To date, the precise molecular and cellular mechanisms of axonal degeneration are under intense investigation. The morphological evidence indicates that axon degeneration as a consequence of aging and neurodegenerative diseases takes place in a retrograde fashion also known as dying back degeneration, which precedes cell death of the neuronal soma. Axon degeneration shares several characteristics with cell death by activation of the necroptotic signaling pathway, including mitochondrial dysfunction, ROS production, and intracellular calcium increase, and we have found that necroptosis inhibition by genetic or pharmacological means delays axonal degeneration in neurons from the peripheral and central nervous systems, as well as in model of Alzheimer´s and Parkinson Disease.
People involved

Macarena Arrazola
PI collaborator

PhD in Biological Sciences from the Catholic University of Chile. Studying the contribution of necroptosis in the age-associated axonal degeneration of the hippocampus, and the impact of using pharmacological approaches to revert neuronal dysfunction and cognitive impairment during aging, proposing necroptosis as an attractive target for the future development of geroprotective tools to treat age-related disabilities.

Daniela Rebolledo
Senior Research Assitant

BI am a Biochemist from Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile (PUC) and PhD in Cell and Molecular Biology from the same university. My PhD thesis research was performed at the Physiology and Biophysics department, University of Washington. My research has focused on the physiology of the neuromuscular system and the pathological mechanisms behind neuromuscular disorders of diverse etiology.

Laura Gomez
Research Assitant

Medical Technologist from the U. Mayor. With experience in histological techniques, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, biochemistry and molecular biology techniques. I am currently working on the role of RIPK3 in axonal degeneration in genetic models of Parkinson’s Disease , through Michael J. Fox’s project.

Rodrigo Leiva
Research Assitant

B.Sc(hons) degree in Neuroscience from the University of Glasgow and M.Sc in Integrative Neuroscience from the University of Edinburgh. I’m currently working on the role of axonal necroptosis and inflammation in the dopaminergic neurons of the nigrostriatal pathway in Parkinson’s Disease to assess it as a potential therapeutic target through the inhibition of RIPK3.
Related Publications
PUBLICATIONSDataCNSNeuroDegenerationAGING
octubre 7, 2021
The necroptosis machinery mediates axonal degeneration in a model of Parkinson disease.
Oñate M, Catenaccio A, Salvadores N, Saquel C, Martinez A, Moreno-Gonzalez I, Gamez N, Soto P, Soto C, Hetz C, Court FA.
Cell Death Differ. 2020 Apr;27(4):1169-1185. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0408-4. Epub 2019 Oct 7.
PMID: 31591470
PUBLICATIONSDataNervous System FxPNS
octubre 7, 2021
The p75NTR neurotrophin receptor is required to organize the mature neuromuscular synapse by regulating synaptic vesicle availability.
Pérez V, Bermedo-Garcia F, Zelada D, Court FA, Pérez MÁ, Fuenzalida M, Ábrigo J, Cabello-Verrugio C, Moya-Alvarado G, Tapia JC, Valenzuela V, Hetz C, Bronfman FC, Henríquez JP.
Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019 Sep 12;7(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0802-7.
PMID: 31514753
PUBLICATIONSDataNervous System FxPNS
octubre 7, 2021
c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent internalization and Rab5-dependent endocytic sorting mediate long-distance retrograde neuronal death induced by axonal BDNF-p75 signaling.
Escudero CA, Cabeza C, Moya-Alvarado G, Maloney MT, Flores CM, Wu C, Court FA, Mobley WC, Bronfman FC.
Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 15;9(1):6070. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42420-6.
PMID: 30988348
octubre 7, 2021
Non-canonical function of IRE1α determines mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum composition to control calcium transfer and bioenergetics.
Carreras-Sureda A, Jaña F, Urra H, Durand S, Mortenson DE, Sagredo A, Bustos G, Hazari Y, Ramos-Fernández E, Sassano ML, Pihán P, van Vliet AR, González-Quiroz M, Torres AK, Tapia-Rojas C, Kerkhofs M, Vicente R, Kaufman RJ, Inestrosa NC, Gonzalez-Billault C, Wiseman RL, Agostinis P, Bultynck G, Court FA, Kroemer G, Cárdenas JC, Hetz C.
Nat Cell Biol. 2019 Jun;21(6):755-767. doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0329-y. Epub 2019 May 20.
PMID: 31110288
Related News
¿Revertir el envejecimiento del cerebro es posible? Estos científicos chilenos aseguran que sí
abril 27, 2023
El “momento Eureka” fue así: en su laboratorio en la Universidad Mayor, el biólogo Felipe Court (47), junto a la científica Macarena Arrazola, testearon en un grupo de ratones de más de 2 años…
U. Mayor recibirá financiamiento para 13 nuevos proyectos Fondecyt Regular
enero 23, 2023
La institución aumentó su número de proyectos seleccionados por la Agencia Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo (ANID) más del doble con respecto al año pasado. El resultado “refleja que nuestro…